Start with co-founding clarity and a lever for growing matters most when you align a team’s energy on an ecosystem that serves developers and learners. dave helped set this direction, keeping the focus on rapid learning and practical outcomes, with being nimble as a core habit.
Over years und months, the team refined the product through tight feedback loops. dave quit a previous role to focus full-time, and the effort werent content with small bets; it helped growth and doubled impact at each milestone, creating an exciting period for the team.
The tech strategy fed the massive ecosystem with AI-assisted features. The team explored gpt-3 powered tooling to accelerate coding sessions, which kept users rapt and returning. That experimentation knowledge and learning process became a lever for expanding usage across languages and platforms.
Strategic partnerships widened reach. codecademy and similar platforms exposed learners to Replit’s editor, turning experimenting into structured practice. The growth model relied on adding dozens of integrations, which doubled the rate of new signups during a critical year and kept the team excited about an exciting trajectory.
Key lessons emphasize disciplined co-founding, continuous knowledge sharing, and a bias toward action. Build a simple, scalable product first; scale by unlocking community energy, then reinvest in core capabilities. The result is a massive network of builders, teachers, and students who contribute back, creating a feedback loop that sustains growth for years und months.
How Replit Went from a Side Project to a $1B Business
Focus on a single core product for production coding and ensure it is accessible to college students and professional devs alike. Build a predictable pricing ladder and lean on marketing to reach teams between startups and large orgs.
Adopt a single-minded engineering approach: rewriting flaky components for reliability, invest in a fast, scalable backend, and keep the office culture lean while hiring limited but capable developers. These ides would become the backbone of a platform with instant feedback and in-browser collaboration.
We studied Codecademy and observed enterprise needs; waqar led the engineering push, while Bytedance showed early interest as a partner. Later rounds refined product-market fit and broadened the platform’s reach beyond hobbyists.
Education-focused momentum followed college partnerships and campus programs, with swag and targeted marketing turning students into regular users. The approach kept development tight and the platform accessible across devices, increasing retention and word-of-mouth.
These moves enabled massive growth: the team moved fast, shipped frequently, and captured most of the developer market. With limited resources, the production stack was hardened, security strengthened, and API access expanded to power external tools and communities.
Going strong, the company would cross the $1B threshold by aligning product, people, and partnerships–from waqar’s team to investors like bytedance–transforming a weekend project into a sustainable, profitable platform that remains open to contributions from developers worldwide.
| Phase | Focus | Auswirkungen |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Prototype editor + live collaboration | Tens of thousands of developers using it weekly; early feedback drove rewriting |
| Phase 2 | Scalable hosting, education ties | 100k+ developers; valuation crossed $1B; investor and partner interest from bytedance, codecademy |
| Phase 3 | Enterprise and school licenses; global marketing | 60+ countries; recurring revenue growth; strong retention |
Growth, Strategy, and Key Lessons for Paying Subscribers Only
Recommendation: Launch a two-tier paying plan with clearly defined value, and use a 14-day trial to surface the most impactful features for paying users.
In a crowded world, an articulated pricing ladder helps users see progress quickly and meaningfully. Those who adopt this approach align their beliefs with measurable outcomes, enabling the team to allocate resources wisely and scale roles around subscriber success.
- Pricing, activation, and conversion
- Define tiers: Starter (core tool access) and Pro (team collaboration, real-time sharing, and priority support).
- Target metrics: convert 8–12% of new signups within 14 days; 25–30% of free users start a paid trial; CAC payback within 6–9 months.
- Trial design: provide 14-day full access with in-app progress indicators; show users the value created from coding sessions and problem-solving evolution.
- Onboarding and activation
- Articulated onboarding sequence guides new users through a key use case within the first two sessions.
- Use in-app nudges to demonstrate value: a daily tip, a sample project, and a completion badge to encourage frequent engagement.
- From the first login, highlight the difference between the free and paid tool sets, and tailor messages to coding goals (web apps, API work, data notebooks).
- Retention and value delivery
- Deliver consistent progress: weekly dashboards show completed tasks, pull requests, or successful runs.
- Integrating feedback loops: collect quick surveys after key milestones; act on the most frequent requests within 30 days.
- Role-based access: offer teams a single billing line and per-seat pricing to reduce friction for those purchasing for organizations.
- Content strategy and education
- Publish frequent tutorials and templates that illustrate the real-world creation of projects, aligning with coding journeys similar to codecademy.
- Showcase case studies from customers who use the platform for projects inspired by gagan, emphasizing tangible outcomes.
- Offer a library of sample projects, problem sets, and reproducible repos to shorten time-to-value.
- Measurement, governance, and growth loops
- Track ARPU, churn, and LTV; monitor CAC and time-to-first-value by cohort; adjust pricing if payback slips beyond 9 months.
- Frequent experiments: test price anchors, feature bundles, and prompts to upgrade; use a combinator approach to evaluate multiple levers in parallel.
- Articulate the resourcefulness behind product decisions; show customers how the changes affect their workflows to reduce guesswork.
Key lessons: focus on those who already show intent, not those browsing casually. Growth derives from solving a real problem with a lean ecosystem of tools, not gimmicks. By integrating customer feedback and product metrics, you transform beliefs into predictable progress and create value that is worth paying for.
From Side Project to Daily DevTool: Origins, PMF, and Early Traction

Recommendation: validate PMF in 30 days by isolating these three core tasks developers perform daily and tying them to a single activation metric. Shaving the feature scope to the minimum viable set could accelerate learning and enable faster decisions that move you ahead. Using a right, articulated metric keeps teams aligned and makes success easy to communicate.
Origins: born as a side project after hours, the tool started with a simple script that saved time on repetitive setup. Open feedback from educators and a single group of early users shaped a narrow, practical base. In a single moment, the idea matured into a product with reality and a path toward broader adoption.
PMF articulation and early signals: the team mapped tasks to outcomes such as faster onboarding, fewer context switches, and clearer roles for team members. Video onboarding and lightweight templates boosted adoption, while these data points guided iteration. three-quarters of early testers came from educators and students, making a strong case that the tool fits workflows in classrooms and labs. The articulated use case helped teams see exactly how the tool fits their workflow.
Early traction metrics: in the first 12 weeks, 4,500 signups produced 800 daily active users, and a 15% conversion rate to paid plans. Retention hit 40% after two months, while 60% of paid users cited productivity gains as the main reason to stay. According to these numbers, the data pointed to a strong signal for PMF, and the team could prioritize features that users could deploy quickly–something tangible to show users. Using these results, the team added core features and kept the roadmap focused on the base needs of developers.
Key lessons and actionable steps: align to a single, clearly articulated use case that covers the ends of daily dev work; keep the base open to educators and teams; monitor competitors, but move faster by shaving nonessential features; communicate benefits through short video clips and real-world examples; plan ahead for scale by documenting roles and creating a fast feedback loop with users. These steps could help teams move from idea to daily practice, whatever their setup, right away, though you may face skeptics.
Monetization Milestones: Pricing, Plans, and Revenue Model Evolution
Recommendation: start with a three-tier pricing stack: Free, Pro, and Enterprise, and back it with annual billing that offers a discount. Define concrete outcomes for each level: Free covers core editor use, Pro unlocks collaboration and higher limits, Enterprise adds governance, SSO, and priority support. This structure gives everyone a clear value path and creates a predictable means to forecast revenue while the team drives execution with focused working discipline. At this moment, collect enough feedback from early adopters to validate the pricing and determine what value signals are worth sharpening; this helps the plan scale, and this path is exciting and offers a real means to measure impact. You should think about what the price meant to users in their own context, and prepare to iterate.
Behind the pricing lies crisp execution: set precise features and limits per tier, define API quotas, onboarding steps, and support windows. Pro includes higher API quotas, advanced collaboration, and analytics; Enterprise adds SSO, audit logs, dedicated success manager, and custom SLAs. Use per-user or per-seat pricing for teams, plus overage charges or usage-based add-ons. Offer annual plans with a two-month discount to lock in value and smooth cash flow. thats next milestone for other teams as well. This approach really clarifies incentives for their roles and helps everyone stay aligned.
Revenue model evolution centers on alignment between customer value and revenue streams. A core question for leadership is how much to invest now versus later. Start with subscriptions and a small API revenue line; eventually, add value via openai integrations and paid features that reflect usage. New opportunities come from partnerships and licensing paths for education, agencies, and open-source projects. Track metrics like churn, ARPU, and lifetime value; funding rounds come when the data shows traction. The goal is three years of disciplined growth and steady profitability, not just buzz.
Beyond core pricing, diversify revenue with languages-focused content and a monetized education path. A ghostwriter-like content engine can produce documentation, templates, and example projects in multiple languages, accelerating adoption while building paid assets. This approach also supports international reach and reduces localization friction. The cambium of the product–its growth engine–depends on beliefs about user value and a practical path to revenue that everyone can buy into. Their feedback loops matter to refine features and pricing.
Growth Engine Playbook: Viral Loops, Partnerships, and Community Adoption

Launch a 4-week viral loop that rewards referrals with 30 days of premium features and a visible badge; track invites daily and target a 5% conversion from referrals in the first month. Keep rules narrow and clear so users know what to do and what they gain. amasad notes that the moment a user shares, the network begins to grow, so design rewards that feel tangible and scarce rather than noisy.
Partnerships amplify reach: secure 4 strategic collaborations in the first year with coding bootcamps, teacher networks, and platform ecosystems. Each partner provides a starter project and co-branded tutorials, giving teenagers and classroom communities a clear path to building. Use open APIs and developer tools to simplify integration and measure joint funnel performance on a shared dashboard. According to partner data, these alliances lift signups from external channels by 3–6x compared to solo campaigns.
Community adoption: run monthly challenges that align with class projects, spawn ambassadors from student clubs, and publish approachable knowledge bites. A ghostwriter can craft friendly guides and templates so beginners see fast wins. Starting with a 6-week pilot in 3 schools, track participation and feedback to keep the momentum and refine the experience based on real-class needs.
Measurement and iteration: define metrics such as activation rate, weekly active users, referrals per user, retention, and withdrawals of credits. Build a track per channel and run monthly A/B tests. Use a simple dashboard to share progress with everyone and keep the founder’s vision open for feedback and adjustments.
Product, tools, and engineering: keep the platform lean while scaling capabilities; lean on openai for suggestions and a robust knowledge base; ensure the API remains open enough for partner tools; invest in a ghostwriter to craft templates and class materials; emphasize security and privacy to sustain long-term trust and growth.
Starting with the right people and roles: define a clear structure including founder, growth lead, engineer, educator, and student ambassador; set a two-quarter cadence for experiments and reviews; keep an open feedback loop so everyone can contribute to smarter decisions and faster iteration.
Product and Platform Strategy: Collaboration, IDE Enhancements, and Integrations
Recommendation: Invest in a collaboration-first browser-based IDE with real-time co-editing, inline conversations, and a modular integrations layer. Ship frequent updates aligned with developers’ timing, so feedback translates quickly into features. This edge comes from turning ideas, writing, and conversations into action inside a single workspace, making something tangible emerge and delivering benefits with minimal friction for the maker community.
Strategy: prioritize three tracks–collaboration UX, IDE enhancements, and external integrations. Start with browser-based live cursors, shared terminals, and task-based comments, plus an API for plugins. Expand integrations with GitHub and bytedance partner services, and cultivate talesbox as a centralized docs and demos surface. Let the most engaged developers, including teenagers, explore paths to contribute, with frequent updates that show meaningful benefits in minutes rather than days.
A leadership note: amasad says the path to scale lies in treating developers as creators, not merely users, and in inviting ideas from the earliest testers–including teenagers. karen reinforces design discipline, ensuring the editor remains approachable for beginners while offering power users room to grow. The october sprint started with core collaboration features, and the feedback loop keeps the team single-minded about reducing friction at every stage.
Action plan for the next cycle: launch a beta of live collaboration, polish the plugin API, and integrate talesbox as a docs hub. Ship something tangible in each release, with a clear sign of progress that users can see in minutes. Bytedance and apple testers will help refine onboarding; we have invested in a broader developer program that includes teenagers and students. Measure impact via session length, number of conversations per file, and the rate from ideas to done. The goal is to boost collaboration speed and reduce context switching while delivering real benefits for teams that code daily.
Scaling Operations and Leadership: Hiring, Culture, and Scalable Processes
Prioritize scalable hiring and onboarding: publish a 30‑day onboarding playbook, build a standard 6‑stage interview loop, and run a weekly report on recruiting metrics to keep the team fast and aligned.
For the hiring engine, design a right, repeatable process that your team can follow in production mode. Use a combinator‑style playbook that blends structured interviews with a shared scorecard, so your recruiters and managers are able to make decisions sooner, not later. In October we tested a prototype of this loop, shaving days off time‑to‑hire and delivering clearer feedback to candidates and teams.
Culture is a system, not a slogan. Codify rituals that reinforce ownership, psychological safety, and fast conflict resolution. Create a weekly touch point between engineers, product, and marketing to close the loop on user feedback, marketing plan, and product roadmap. This keeps your company aligned with reality, not just intent, and helps every user feel heard as the product scales.
- Hiring: standardize job briefs, use a shared interview rubric, and rotate interviewers across teams to avoid bias. Implement a prototype of onboarding tasks that can be completed within the first 2 weeks to demonstrate impact in production.
- Onboarding and ramp: zip through a 4‑week ramp with clearly defined milestones, hands‑on tasks, and a shadowing period with a senior teammate. Measure progress with concrete outcomes and a simple report on what the new hire wrote, built, or tested.
- Culture and leadership: publish core values as actionable guidelines, not posters. Run quarterly feedback cycles and public recognition to reinforce behavior that drives speed and collaboration.
Scalable processes turn teams into a company that can run with minimal friction. Create SOPs for core workflows–from code reviews to production deploys–and archive them in a central wiki that everyone can access via ides or common development tools. This means you can onboard a new hire, and even a new team, faster and more consistently.
Leadership plays a critical role in the scale narrative. Lead with a person‑first approach and empower managers with a transparent decision framework. Align with founders and mentors, including voices like amasad, who push for an interpreter mindset: decode feedback quickly, iterate, and write clearer guidance for the next cycle. In practice, this leads to faster decisions and a tighter feedback loop that ends the guesswork around priorities.
You should measure velocity not only in hiring but in sustained productivity. Use a report that tracks time from offer to start, first 90 days’ outcomes, and the share of production time spent on critical work. If a metric stalls, treat it as a challenge to be solved with a targeted adjustment–whether it’s refining interview prompts, adjusting onboarding tasks, or reallocating early responsibilities to a capable interpreter‑level teammate.
Case in point: our team used a prototype for the onboarding flow, then refined it with real user (engineer) feedback. The result was a faster ramp, more predictable output, and a clear path for the next hires. The fact is, scalable hiring and culture are not magical; they are built with disciplined processes, concrete milestones, and constant iteration–the same discipline that powered replits to a stronger operating rhythm.

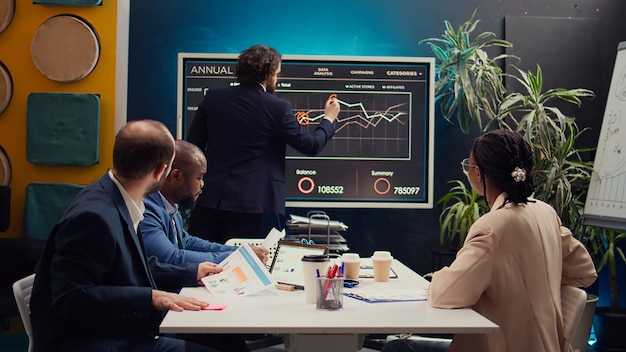 How Replit Went from a Side Project to a $1B Business – Growth, Strategy, and Key Lessons">
How Replit Went from a Side Project to a $1B Business – Growth, Strategy, and Key Lessons">
Kommentare